Balancing Cost and Performance for Bolt Coatings
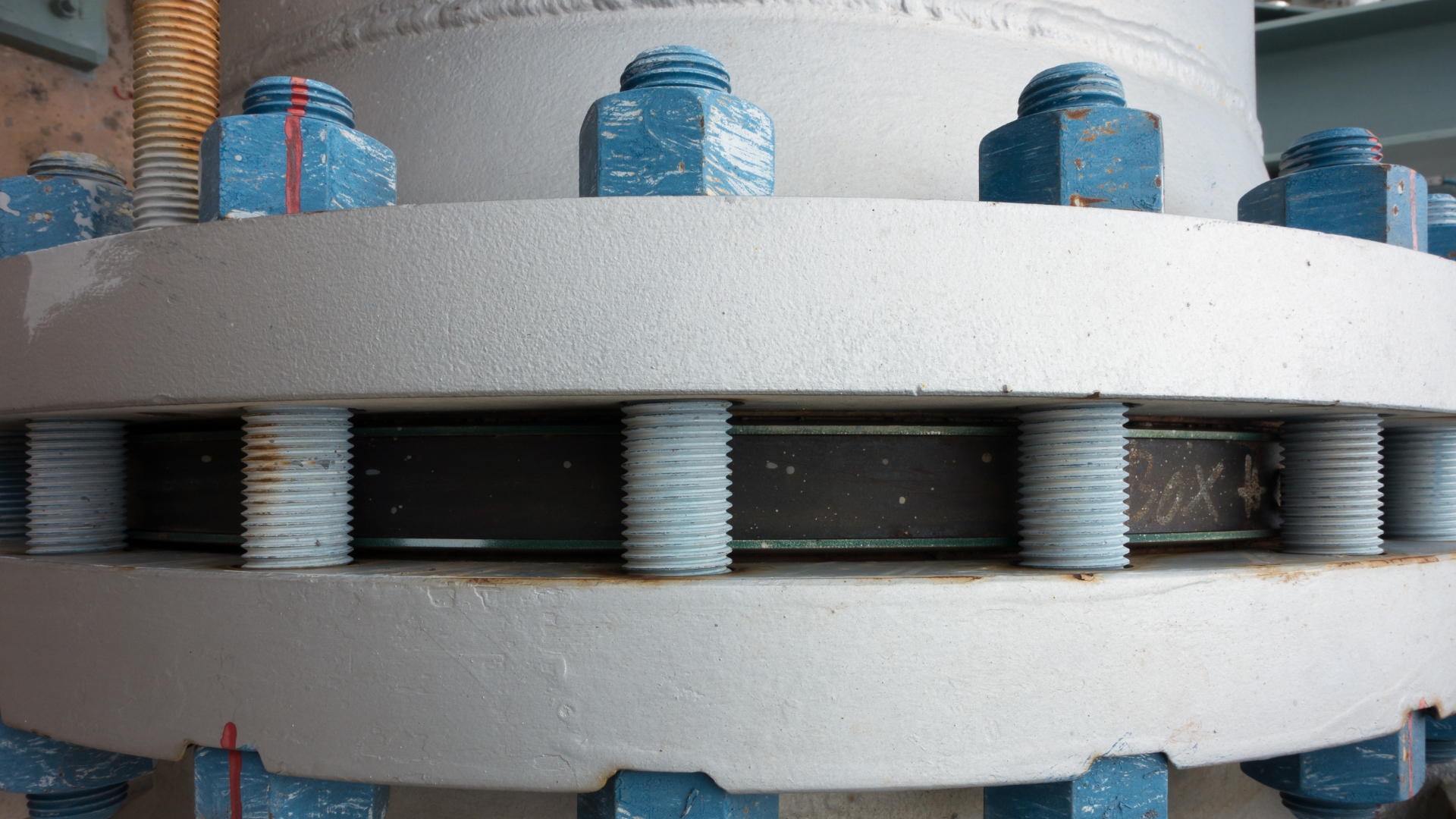

Selecting the most effective bolt coating for your application can have a major impact on corrosion protection performance, maintenance time, and budget. The primary function of bolt coating is corrosion protection during transport, storage, and service life of the fasteners. When selecting a coating material, you should consider a range of factors: location, temperature, application, and weather conditions. For example, bolts in a high-temperature or heavy salt-spray environment will need a higher-performance coating than bolts being used in an indoor, temperature-controlled environment.
Benefits of Proactive Investment in Bolt Coating
Bolt coating selection makes a big impact on future maintenance cycles. If bolts are adequately protected against corrosion and temperature, disassembly of the connection could be easily done. However, if the bolts seize from built-up oxidation or corrosion, the connection would have to then be cut loose, which means additional work permits, extra time, and added cost. Although cutting fasteners loose is often considered a routine part of these maintenance cycles, the associated costs of future delays, labor, permitting, and tooling often outweigh the initial savings of choosing a less protective (and less expensive) coating.
When selecting a bolt coating material, there is generally a tradeoff between cost savings and performance. To find the right balance, it is important to identify where your application fits on the spectrum between lowest cost and highest level of protection. Keep reading for an overview of the types of bolt coating materials, as well as their relative cost and benefits.
Zinc and Cadmium
Zinc and cadmium are both used to add a thin layer of corrosion protection to a fastener. Zinc and cadmium are sacrificial coatings that protect the bolt by corroding faster than the bolt material underneath. These relatively low-cost coatings will keep your components from rusting during transport and storage (particularly in an indoor or climate-controlled environment). For most applications, these coatings will not provide adequate protection during the actual service life of the bolt.
Zinc Nickel
In terms of corrosion resistance and price, zinc nickel is one step above zinc and cadmium. It combines the sacrificial coating properties of zinc with the relative strength and corrosion resistance of nickel. It can be used for protecting bolts during transport and storage, as well as during actual service life of less corrosive application environments.
Zinc Flake
Zinc flake offers intermediate corrosion resistance at an intermediate cost. This coating consists of a mixture of zinc and aluminum flakes. It generally creates fewer corrosion byproducts than other types of zinc coatings, and it also offers better protection against hydrogen embrittlement. Zinc flake provides enough resistance to corrosion from phosphates or soil content to make it a good choice for applications such as automotive or wind energy foundation bolting. However, zinc flake does not offer enough protection in heavy salt spray or extremely high-temperature environments.
PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) coatings offer reliable resistance against abrasion and corrosion, adding low friction and non-stick properties on top of the bolt’s base material. PTFE can benefit the bolt installation process by reducing friction and galling. During service life, PTFE provides effective protection against more corrosive weather conditions. Since it holds up under heavy salt spray, this coating is suitable for offshore and near-shore applications. However, PTFE should not be used in high-temperature applications.
Nano Galvanized
Nano galvanized coatings improve the performance of other galvanic coatings by combining a sacrificial coating (like zinc) with nanoparticles or nanofibers that improve adhesion and corrosion resistance. This also makes it possible to apply a thinner coating that still protects bolts in highly corrosive and relatively high-temperature (750°F) environments.
Nickel-Cobalt
Nickel-cobalt offers top-tier corrosion resistance and the highest temperature rating. Nickel and cobalt form a hard, conductive coating that resists corrosion, prevents hydrogen embrittlement, and withstands temperatures up to 1,300°F. This electroplated coating comes at a premium price, which means it is most often used only in extreme application conditions such as near-shore oil refineries.
Choosing the Right Coating Has Long-Term Benefits
To find the right balance between the cost and performance of your bolt coating, keep in mind that upgrading to a higher level of performance can pay major dividends by helping you reduce cost, avoid delays, and decrease maintenance workload. Regardless of your application, the experts at Lamons are here to help you choose the coating material that will fit your budget and performance requirements.